Motors are electronic devices that converts electricity into mechanical rotary power. They are made of coils of copper wire wound on a laminated iron supported by ball bearings and placed in between two strong magnetic field. When current is applied to it it rotates due to the attraction and repulsion set on on each ends of the armature which then constitutes a couple.
Motors consists of parts which are bearings, armature, magnets, connectors and casing.
Parts of an electric motor.
- Armature. It is made from bundles soft iron sheets separated by non conductive gels and packed together into what is called a laminated iron core. The lamination of armatures helps to reduce eddy current losses. The armature consists of insulated copper wire wound on it. When current is passed to the coil, the armature becomes a strong electromagnet which is then repelled and attracted by permanent magnets forming a rotation.
- Connectors. They are use for connecting the armature coil to external circuits or a power source. Connectors are usually made of graphite also known as carbon brush.
- Magnets. They are use for providing magnetic field flux. Most heavy motor's permanent magnets are replaced with electromagnets because their magnet flux can be increased and don't fade out like the permanent type.
- Casing. Motors are usually cased from dust,liquids and electromagnetic interference. Motors are cased with iron in cylindrical form to form a Faraday cage for reduction of electromagnetic interference from external sources.
- Bearings. The armature shaft is built to rotate in two bearings in order to reduce friction which can lead to wear and tears and loss in efficiency of the motor.
There are two types of electric motors namely AC and DC motors. They runs on different types of electric current.
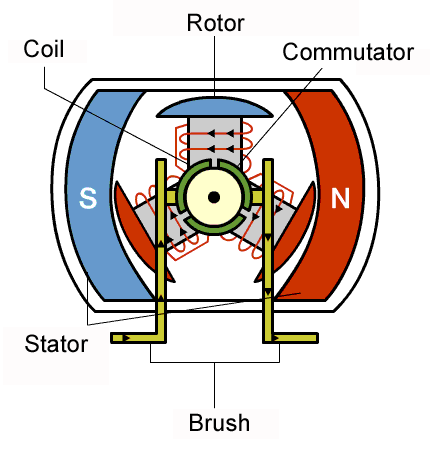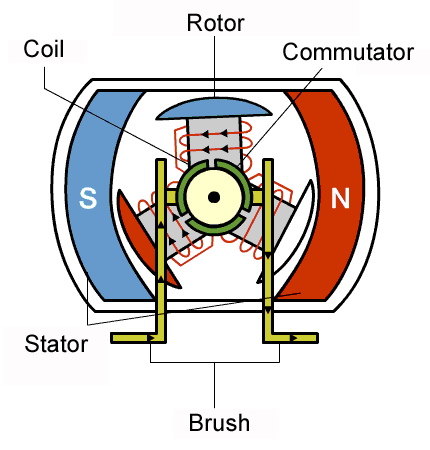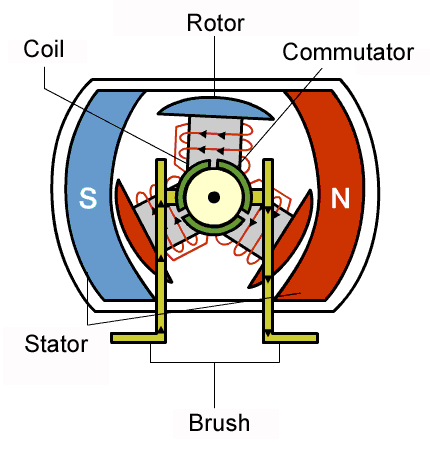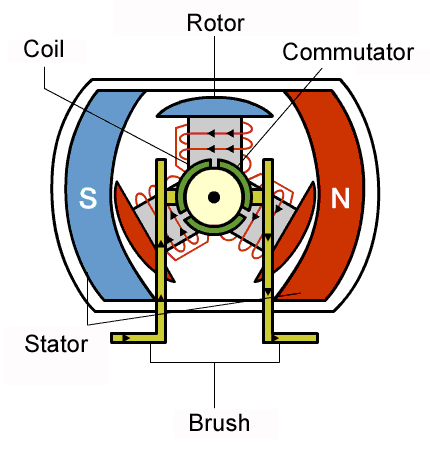
DC motor.
This type of motor works on direct current, therefore it can't be powered with AC. It consists of a rectangluar coil of insulated copper wire known as the armature which can turn about a fixed axis, A powerful magnetic field in which the armature rotation is provided by two curved poles pieces of a powerful magnet, A commutator consisting of split copper ring , two half's which are insulated from each other. Each end of the coil is attached to each half of the split copper ring and two carbon brushes which are made to press Lightly against either side of the split-ring commutator.
Working principles of a DC motors.
When direct current is passed to the armature of a DC motor via the connectors, it becomes magnetised because of the magnetic field created by the copper coil. The magnet field strength depends on the number of copper turns and the amount of current supplied to it. One pole of the armature becomes the north pole when current flows out from it coil and the other side becomes the south pole because current flows in there through the coil.
AC motor.
An AC motor converts alternating current into rotary movement of it armature or a permanent magnet. It is made of a permanent magnet as the rotor, the field coil as the stator and a slip spring.
Working principles of an AC motor.
It consists of a stator coil and a permanent magnet. When alternating current flows through the stator coil, a varying magnetic field is produced. The permanent magnet placed inside the stator coil begins to rotate at high speed depending on the frequency and amount of AC passed through the stator coil.
Tags:
Basic Electronics